Opis
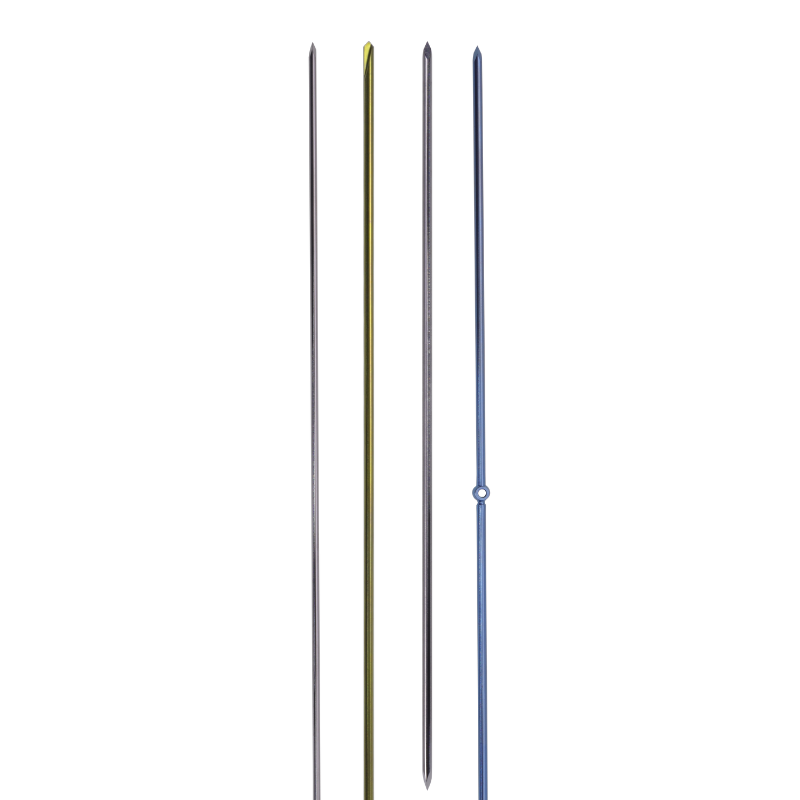
Kirschner Wire
Q&A
Q1: What is a Kirschner Wire (K-wire) and what is its primary purpose?
A1: A Kirschner Wire (K-wire) is a sharp, smooth stainless steel or titanium alloy pin used in orthopedic surgery. Its primary purpose is to provide bone fragment stabilization, acting as a temporary internal splint to hold bone pieces in place during fracture healing or after a corrective osteotomy.
Q2: What are the different types of K-wire tips?
A2: K-wires primarily come with two tip designs:
Trocar Point: A sharp, three-faceted point that is self-drilling and ideal for most applications.
Diamond Point: A sharper, spade-like point that is not self-drilling and requires a pre-drilled pilot hole, often used in hard cortical bone to prevent skidding.
Q3: What are the most common risks and complications associated with K-wires?
A3: The most common complications include:
Pin Tract Infection: The most frequent issue, where bacteria enter along the wire, causing redness, pain, and discharge.
Wire Migration: K-wires can loosen and move from their original position.
Skin Irritation: The protruding ends can irritate the surrounding skin and soft tissues.
Breakage: Though rare, wires can break under stress.
Nerve or Tendon Damage: During insertion, nearby structures can be injured.
Q4: What factors determine the stability of a K-wire fixation?
A4: Stability depends on the number of wires used, their diameter, the specific placement pattern (E.g., crossed or parallel), and the quality of the bone. Multiple wires are often used to create a stable construct and prevent rotation of bone fragments.
Q5: Can K-wires be used for permanent fixation?
A5: Generally, no. K-wires are primarily intended for temporary fixation due to the risk of long-term complications like migration, breakage, or infection. They are usually removed after the bone has healed sufficiently.
Q6: What are the main advantages of using K-wires over other fixation methods like screws or plates?
A6: Key advantages include:
Minimally Invasive: They can often be inserted through small incisions or percutaneously.
Versatility: They can be used in small bones and fragments where screws or plates are not feasible.
Isplativost: They are relatively inexpensive.
Adjustability: Bone fragments can be manipulated after wire insertion.
Q7: In which specific surgical procedures are K-wires most commonly used?
A7: K-wires are extremely common in:
Hand and wrist surgery (E.g., finger fractures, Colles’ fracture).
Foot and ankle surgery (E.g., bunion correction, toe fractures).
Pediatric orthopedics (E.g., supracondylar humerus fractures in children).
Temporary joint arthrodesis during complex reconstructions.