ລາຍລະອຽດ
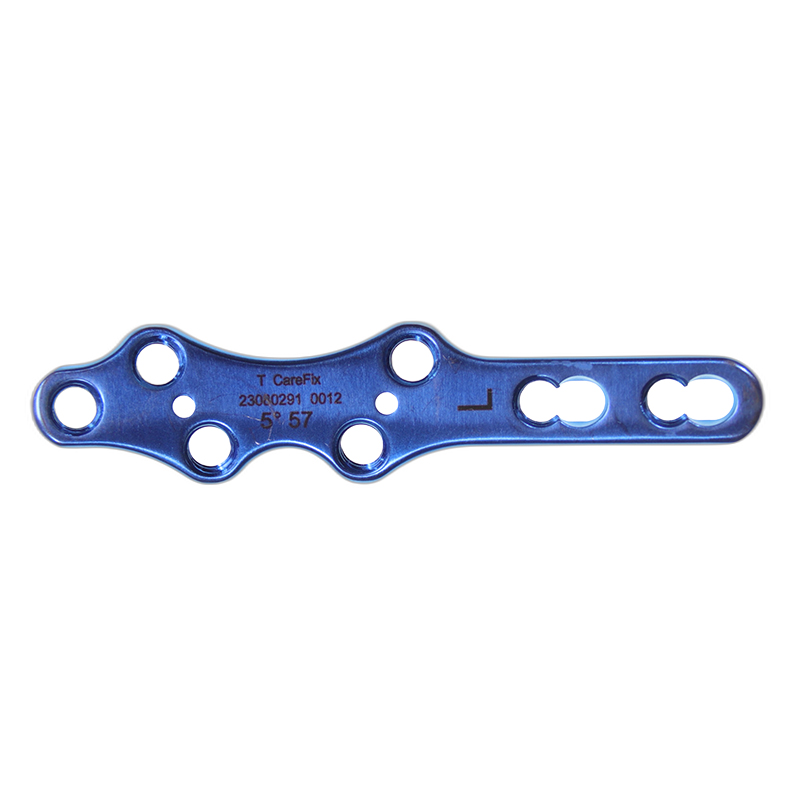
1st MTP Fusion Locking Plate
ຖ່ອງ&ກ
q1: What is a Calcaneus Locking Plate used for?
A1: The Calcaneus Locking Plate is designed for fixation of fractures and deformities of the calcaneus (heel bone), especially intra-articular and comminuted fractures.
Q2: Why is locking technology important for calcaneal fractures?
A2: Locking screws create a fixed-angle construct that provides superior stability in osteoporotic bone and maintains reduction even under high load-bearing stress.
Q3: What material is the Calcaneus Locking Plate made from?
A3: It is typically made of titanium alloy or stainless steel, providing high strength, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance.
Q4: What are the main indications for using a Calcaneus Locking Plate?
A4: Indications include displaced intra-articular fractures, Sanders type II–IV fractures, calcaneal malunions, and corrective osteotomies.
Q5: What surgical approach is commonly used with this plate?
A5: The lateral extensile or minimally invasive sinus tarsi approach is most often used to place the plate along the lateral wall of the calcaneus.
Q6: What advantages does the anatomical design provide?
A6: The plate is pre-contoured to fit the natural anatomy of the calcaneus, reducing soft tissue irritation and ensuring optimal screw positioning.
Q7: How many screw options does the Calcaneus Locking Plate typically provide?
A7: It offers multiple locking and non-locking screw holes for fixation into the posterior facet, anterior process, and calcaneal tuberosity.
Q8: Can this plate be used for both left and right calcaneus?
A8: Yes, it is available in left and right anatomical configurations to ensure precise adaptation to the patient’s bone.
Q9: What are the benefits compared to conventional non-locking plates?
A9: Locking plates provide greater stability, reduce the risk of screw loosening, and maintain fracture alignment even in poor bone quality.
Q10: What is the expected outcome after using a Calcaneus Locking Plate?
A10: Patients typically experience restored heel height and width, improved subtalar joint alignment, and early mobilization with a low risk of implant failure.