1. Distal radius: anatomical definition and structural overview
The distal radius forms the major articular surface of the wrist and contributes to both the radiocarpal joint and the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). The articular surface of the distal radius can be divided into two primary fossae:
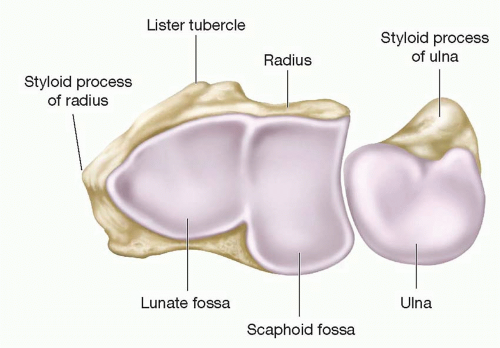
Scaphoid fossa:elliptical in shape and articulates with the scaphoid.
Lunate fossa: more spherical and articulates with the lunate.
Between these is a slight ridge. On the ulnar side is the sigmoid notch (ulnar facing), which forms part of the DRUJ and engages the distal ulna.
The metaphyseal region, 2–3 cm proximal to the radiocarpal joint, is composed predominantly of cancellous bone and flares to form the distal radial metaphysis. Варыяльная кары дыстальнага рад -ius больш тоўстая, чым спінная кара, і валявая паверхня ўтварае частку падлогі запясцевага тунэля.
Важныя структуры мяккіх тканін: Радыякарпальныя звязкі (радыёскафакапітт, радыялунат), трохкутны фіброкартны комплекс (TFCC) З боку локцевага боку, Спінны і валярны рэтынатурны і капсульны ўкладанне; Гэтыя ўплываюць на мадэль і стабільнасць пералому.
2. Рэнтгеналагічныя параметры
Ніжэй прыведзены Commonly выкарыстоўваюцца рэнтгеналагічныя тэрміны і кароткія азначэнні, якія выкарыстоўваюцца для колькаснай ацэнкі дыстальнага радыяльнага выраўноўвання.
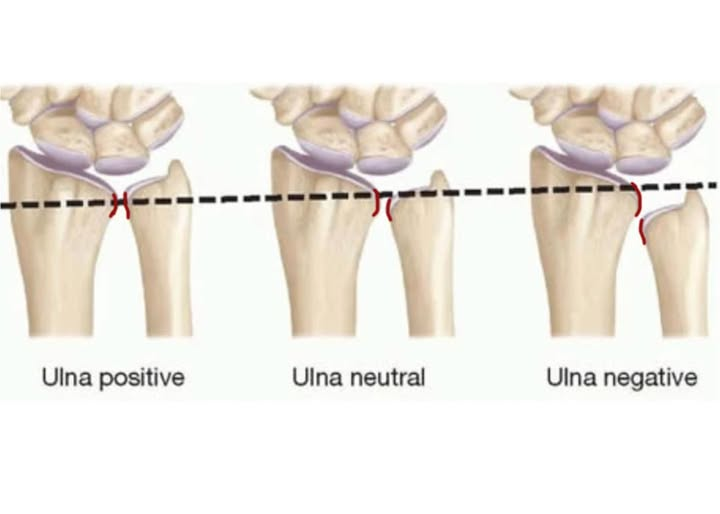
Вулавая дысперсія: адносная даўжыня дыстальнай сустаўнай паверхні лок, вымяраецца на нейтральнай рэнтгенаграме ПА. Дысперсія ўлнара ўплывае на размеркаванне нагрузкі праз запясце.
-Станоўчая дысперсія: Калі лок 1-4 мм. 4 ММ сур'ёзна і патрабуе хірургічнага рамонту.
-Нейтральная дысперсія: Ulnar and radial articular surfaces at the same level
-Negative: Ulna is relatively shorter than the radius
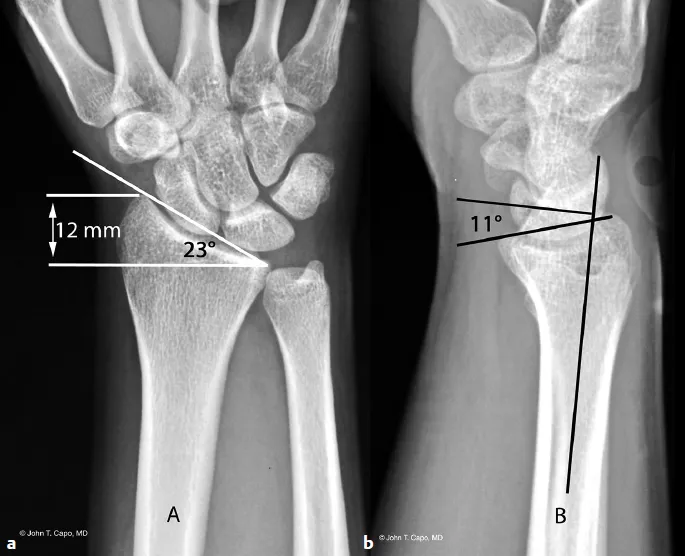
Volar tilt (palmar tilt): the angle formed on a true lateral radiograph between a line drawn along the distal radial articular surface and a line perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the radius. Normal volar tilt is approximately 10–15° volar (palmar). Loss of volar tilt or dorsal tilt is clinically significant.
Radial height (radial length): measured on the PA radiograph as the distance from the tip of the radial styloid to the ulnar corner of the distal radius articular surface (or a consistent reference), usually ~11–12 mm in the normal adult.
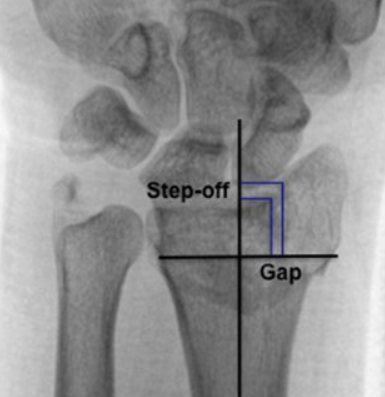
Intra articular step off and gap: direct measures of articular incongruity. Step off refers to a vertical displacement between adjacent articular surfaces; gap refers to a horizontal separation. A commonly used threshold for considering reduction inadequate is an articular step off or gap > 2 мм.
3.AO/OTA classification of the distal radius
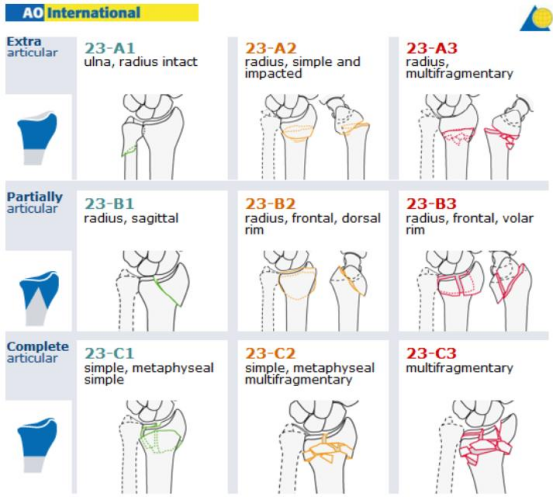
Type A — extra articular fractures
Type B — partial articular fractures
Type C — complete articular fractures (articular and metaphyseal involvement)
Each type is subdivided into groups (1–3) and subgroups; AO C3 denotes complete articular fractures with multifragmentary (comminuted) articular and metaphyseal components — the most complex AO distal radius category.
AO C3 (characteristics and challenges)
High degree of articular comminution with multiple small intra articular fragments.
Metaphyseal fragmentation often with bone voids / impaction.
Associated soft tissue injury and possible DRUJ involvement.
Reduction and stable fixation are technically demanding because small fragments may be difficult to capture with a single volar plate,achieving and maintaining anatomic articular congruity is critical.
CT imaging frequently clarifies fragment distribution and helps surgical planning in C3 fractures.
4. Common regions at risk for loss of reduction
Experience and series data (including case series of single VLP fixation) identify several fragments prone to secondary displacement:
1.Volar lunate facet (lunate fossa) fragments — loss of support here leads to collapse of the central articular surface and subsidence; this was the most common fragment to lose reduction in reported series.
2.Scaphoid fossa - Цэнтральная дэпрэсія або ўрэгуляванне выклікае адступленне ў сустаўнай паверхні скафоіда.
3.Радыяльныя стылоідныя фрагменты - калі не адэкватна паменшаны/выпраўлены, можа мальротаваць альбо спадаць
4.Механізмы страты скарачэння
Неадэкватнае першапачатковае зніжэнне: сустаўнае ўздзеянне не належным чынам узвышана і не спакавана.
Памылкі размяшчэння пласціны: пласцінка, размешчаная занадта радыяльна/праксімальна, можа прадухіліць падтрымку дыстальных шруб
E Lunate Facet альбо можа прапусціць невялікія валявыя фрагменты.
Недастатковая купля шрубы ў невялікія фрагменты: дыстальная траекторыя шрубы і даўжыня не аптымізавана.
Страта косці / метафізальная пустэча: без прышчэпкі або замены косці, можа адбыцца прасяданне.
Дрэнная якасць косці (астэапароз): Зніжаная магутнасць шруб.
Surgeons should pay special attention intraoperatively to confirm containment of the lunate facet and to assure the distal screw trajectory supports key fragments.
5. Surgical approaches: selection, schematics and advantages
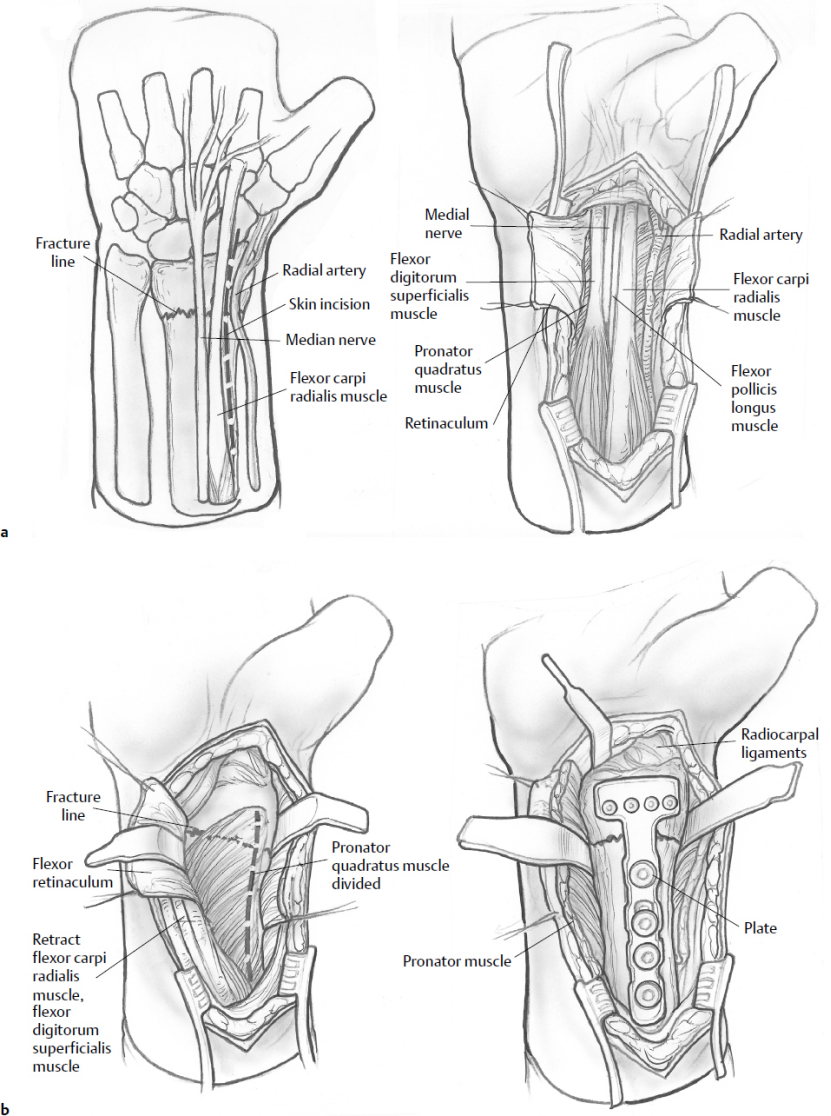
5.1 Extended Flexor Carpi Radialis (FCR) approach / Volar Henry approach
Indication: Most common volar approach for distal radius fractures; allows exposure of scaph
oid and lunate fossae and volar fracture fragments.
Technique highlights: skin incision centered over the FCR sheath, retract FCR and flexor tendons ulnarly, incise and reflect pronator quadratus to expose the volar distal radius. The extended FCR provides additional radial exposure toward the radial styloid. The modified Henry variant goes between FCR and radial artery.
Перавагі:
Direct access to volar articular fragments (у тым ліку Volar Lunate Facet, калі досыць вялікі), Пранатар Quadratus забяспечвае васкулярызаванае засланку для пакрыцця пласцінак.
Нізкі рызыка раздражнення сухажылляў разгінальніка ў параўнанні з дорсальнымі падыходамі.
Звыклая экспазіцыя для нанясення пласцін для замацавання Volar.
Абмежаванні:
Абмежаваная візуалізацыя дорсальных фрагментаў; можа не дасягнуць дорсальна перамешчанага / Фрагменты спіннога абадка.
5.2 Локцевы падыход да дыстальнага радыусу
Indication: Пераломы Volar Ulnar Courn, Доступ да сігмападобнай выемкі/druj, Volar ulnar Comprincy, альбо калі патрабуецца ацэнка/рэканструкцыя DRUJ.
Technique highlights: разрэз паміж локцевым нервова -сасудзістым пучкам і змесціва; Дазваляе добрую візуалізацыю Volar Ulnar Corner і Sigmoid Notch.
Перавагі:
Прамы доступ да калоны Volar Ulnar і сігмападобнай вышыні, Карысна для вырашэння сустаўных фрагментаў і паталогіі Druj.
Абмежаванні:
Больш спецыялізаванае ўздзеянне; Рызыка для локцевых нервова -сасудзістых структур, калі не выконваецца старанна.
5.3 Іншыя меркаванні: Спінны падыходы і камбінаваныя экспазіцыі
Спінны або дорсарадыйны падыход карысныя, калі існуюць вялікія спінныя фрагменты або спінны абадок; спінныя пласціны альбо камбінаваныя спіны + Для стабільнасці могуць спатрэбіцца валявыя канструкцыі.
Камбінаваныя падыходы (механізм + спінны) Часам неабходныя пры цяжкіх пераломах С3, каб зафіксаваць як валявыя, так і спінныя фрагменты.
6. Дыстальная радыусная пласціна LCP Volar
Перавагі
Выпраўлены кут канструкцыі: Шрубы для блакавання ствараюць вуглавую стабільную канструкцыю, якая дзейнічае як унутраны фіксатар і менш залежыць ад якасці костак для пакупкі дыстальных фрагментаў.
Нізкі профіль на валявай паверхні: у параўнанні з дорсальнымі пласцінамі, Паніжаная частата разгінальнай сухажыллі.
Анатамічныя дыстальныя шаблоны: Шматлікія VLP маюць дыстальныя адтуліны для шрубы, арыентаваныя на падтрымку субхандральнай косці люната і скафаідных ям.
Дазваляе ранні рух: з дастатковай фіксацыяй, Пацыенты могуць пачаць ранняе мабілізацыю запясці, што прыносіць карысць функцыянальнаму аднаўленню.
Паказанні
Зрушаныя дыстальныя пераломы радыусу, якія патрабуюць ORIF, дзе Volar падыход забяспечвае доступ да ключавых фрагментаў.
Многія ўнутрысуставыя пераломы, уключаючы некаторыя пераломы AO C3, калі фрагменты можна паменшыць і захоплены пласцінкай канструкцыяй.
Астэапаратычныя пераломы, дзе фіксацыя шруб для фіксацыі.
Супрацьпаказанні
Надзвычай абгрунтаваныя мультыфрагментарныя пераломы, дзе дыстальныя фрагменты занадта мала, каб быць зафіксаваны толькі плітай (напрыклад, Малюсенькія грані Volar Lunate, якія не паддаюцца куплі шрубы пласціны).
Вялікія дорсальныя фрагменты абадка, якія нельга кантраляваць з дапамогай варыяльных шруб - можа спатрэбіцца спінная фіксацыя або камбінаваная пакрыццё.
Cases where plate positioning would inevitably impinge on tendon or joint if applied volarly.
7. Clinical outcomes
Overall success of single VLP in AO C3 fractures: retrospective series show maintenance of reduction to union in about 80–90% of cases when a single VLP is used and when plates are well positioned and fragments are adequately reduced.
Failure patterns: failures concentrate in cases with lunate facet involvement, inadequate distal screw support or plate malposition; some studies report loss of reduction rates from ~3–10% depending on case mix and definitions.
Comparative data: randomized and comparative studies show that combined fixation can offer better initial articular reduction in some highly comminuted patterns but may not yield superior long term functional outcomes and may be associated with higher hardware morbidity.
Note:The copyright belongs to the original author and the magazine,posts are for learning and communication only.