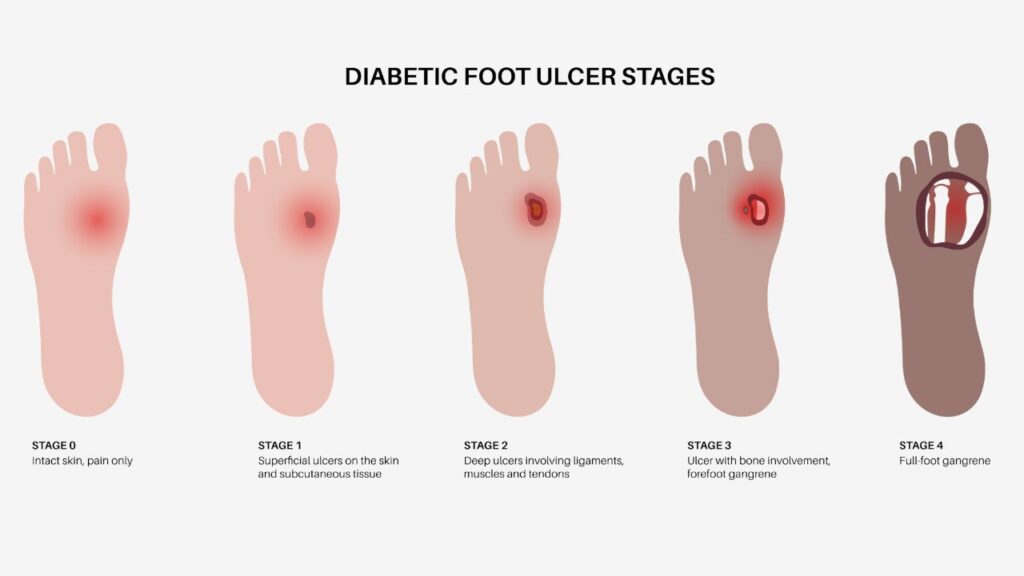
What is Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes, and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, six percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication.Diabetes is the leading cause of nontraumatic lower extremity amputations, and approximately 14 to 24 percent of patients with diabetes who develop a foot ulcer have an amputation.
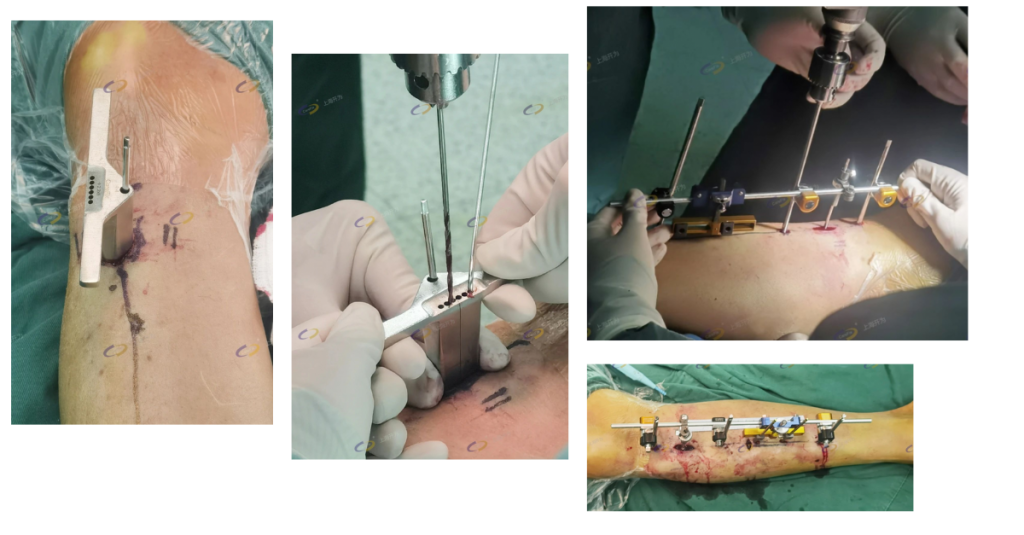
Surgical technique
After administration of general anesthesia or lumbar anesthesia, the osteotomy area was selected as the medial tibial cortex about 10 to 20 cm below the knee joint. After appropriate positioning, the external fixation frame was fixed at the far and near ends of the tibial osteotomy area with two half nails. Two half nails were then placed in the osteotomy area. An approximately 6-cm-long incision was made at the far and near ends of the osteotomy area of the inner tibia, the subcutaneous tissue was separated, and the inner tibia side was exposed. The bone flap was then separated from the tibial backbone with a bone knife after drilling, the external fixation device was assembled, and the complete free bone flap was determined. Finally, the inci- sion was sutured.
Postoperative management
Tibial cortex transverse distraction (TCTD) began 3 to 5 days after the operation and was carried out 1 mm every day for 14 days (Figure B). The daily 1-mm distraction was divided into three time points (morning, noon, and night). The bone mass was then moved 1 mm in the reverse direction every day; this treatment was also divided into three time points (Figure C). If the patient felt intolerable pain, the 1-mm movements were performed every 2 days. After the pain had been obviously relieved, the movements were increased to 1 mm per day. The total distraction time ranged from 28 to 30 days in most patients.An X-ray examination was per formed every month to evaluate the bone healing, and the external fixation frame was removed after initial healing of the bone window.
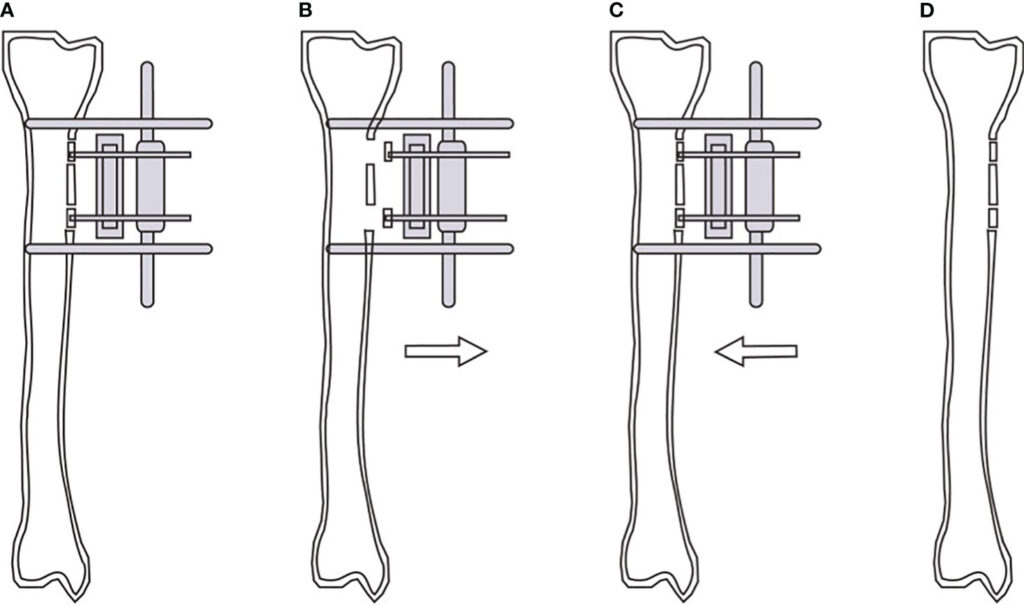
(A)Position of bone windows opening, bone blocks fixation and external fixator screws during operation. (B)Continuous external traction of the bone blocks from the 3-5th day after operation. (C)Reverse traction of the bone blocks reduction after 2 weeks of traction. (D)Removal of the external fixator and gradual healing of the tibial cortex.
CareFix Transverse Tibial Bone Transport
CareFix is a professional national high-tech enterprise engaged in orthopedic medical equipment design, production, sales and service. Founded in 2009, we’ve devoted to pediatric implants,foot & ankle implant,external fixation and spinal implants. Welcome to visit to our factory,it’s about half an hour from Shanghai Hongqiao Airport.